Clustering is an example of unsupervised machine learning, in which you train a model to separate items into clusters based purely on their characteristics, or features. There is no previously known cluster value (or label) from which to train the model.
First create an Azure Machine Learning resource.
After finishing the resource group open Azure ML Studio.
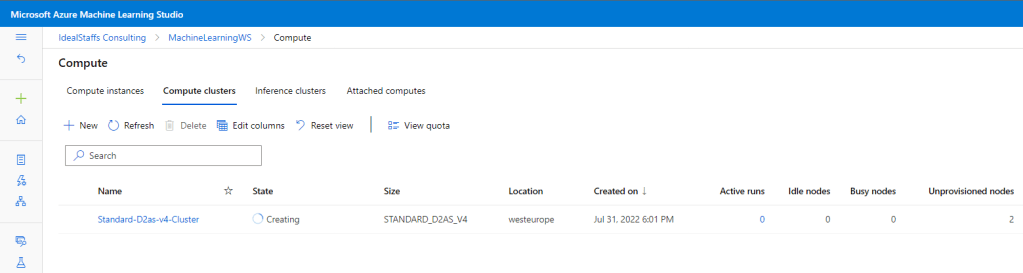
Create a compute cluster
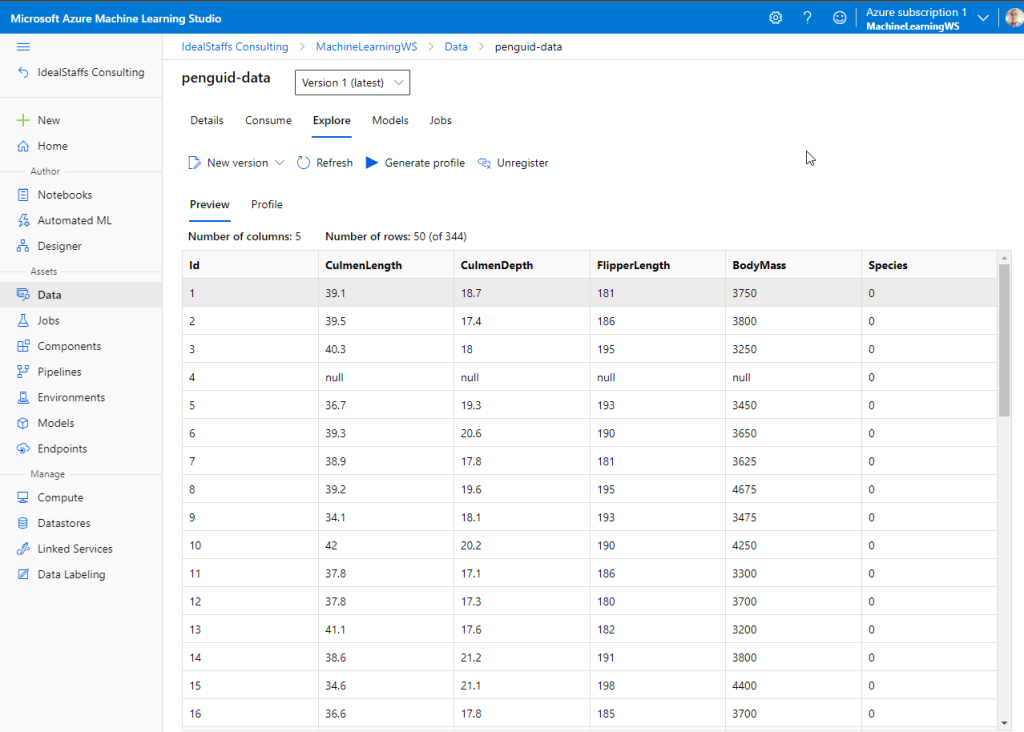
Navigate to Data and create the penguin dataset.


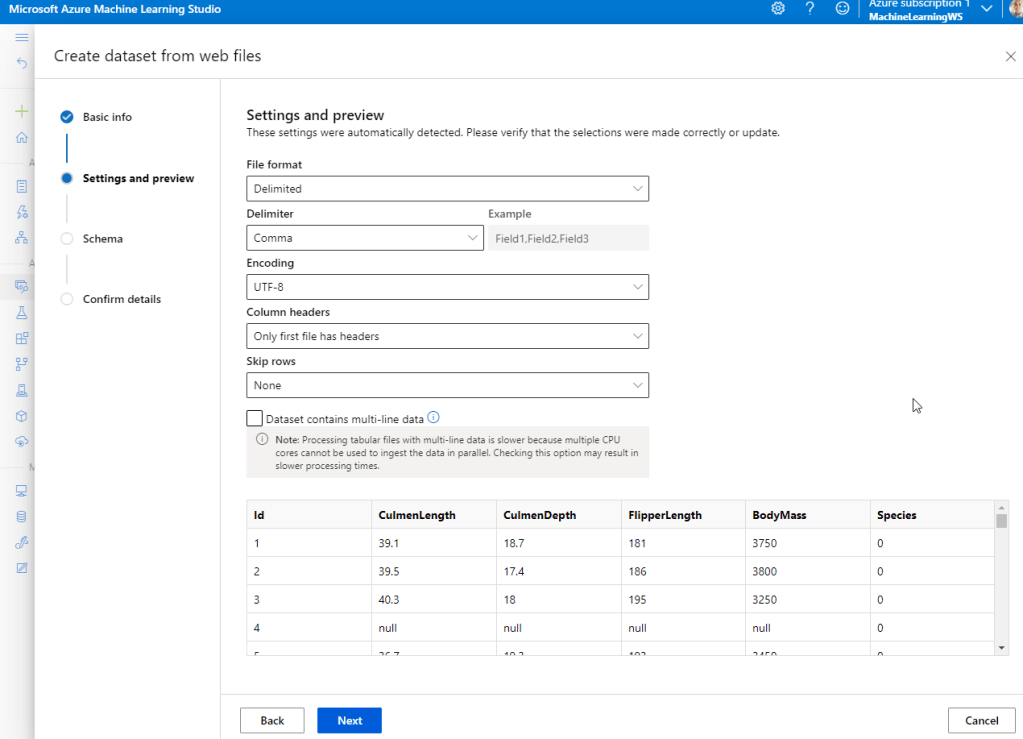
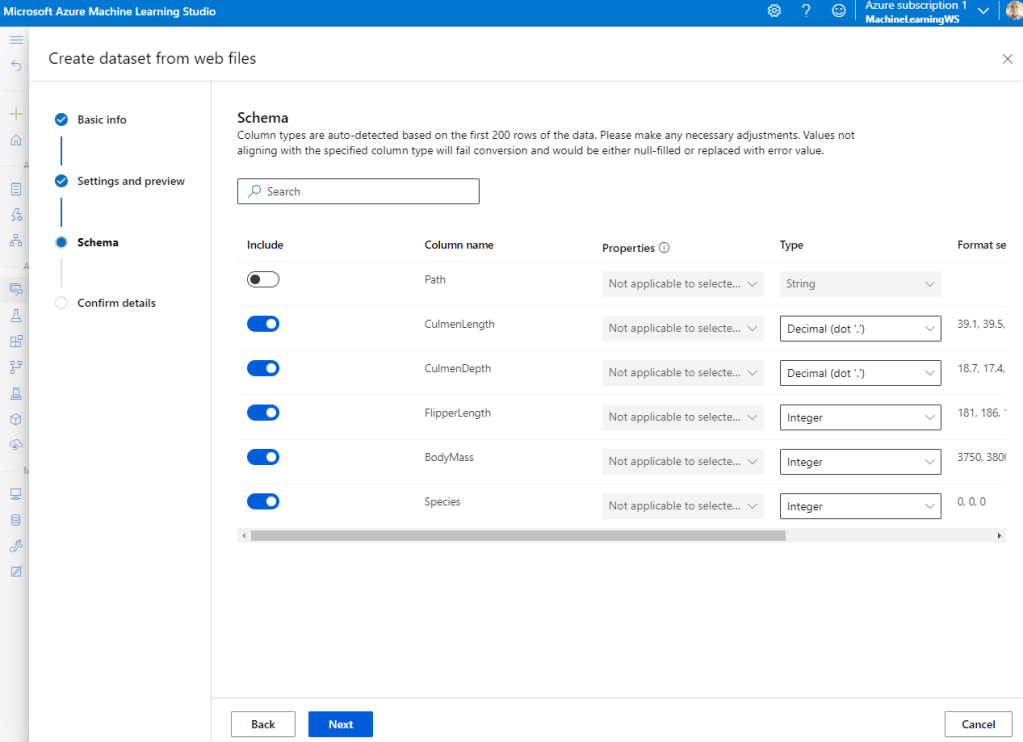
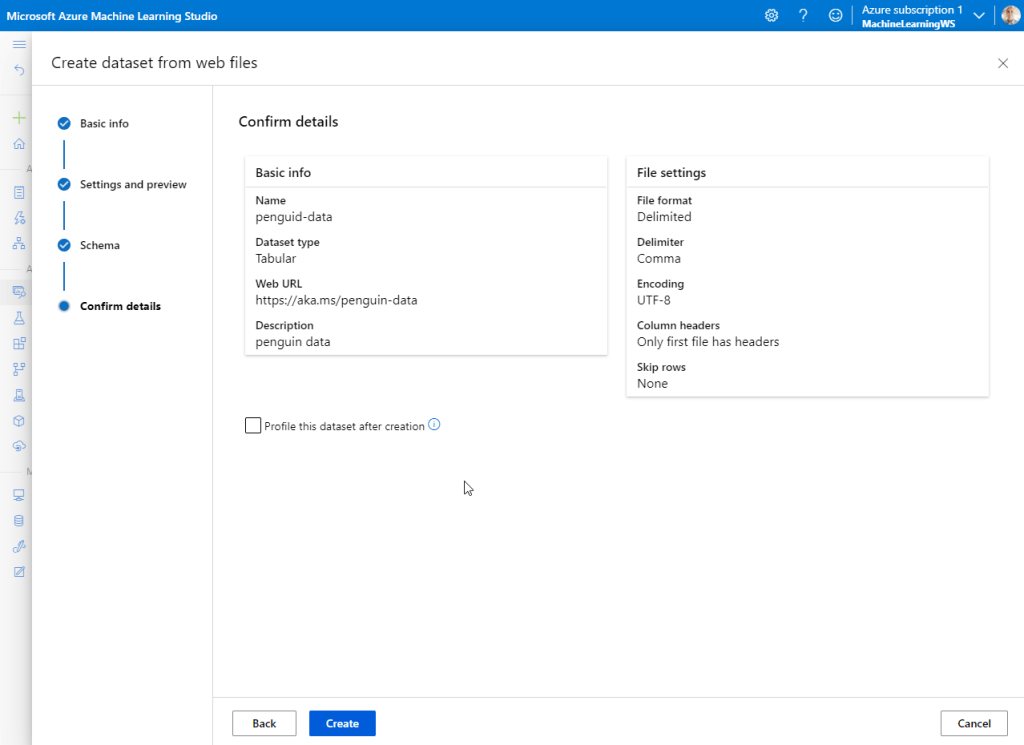
After importing, Explore the data.
Create a new pipeline.
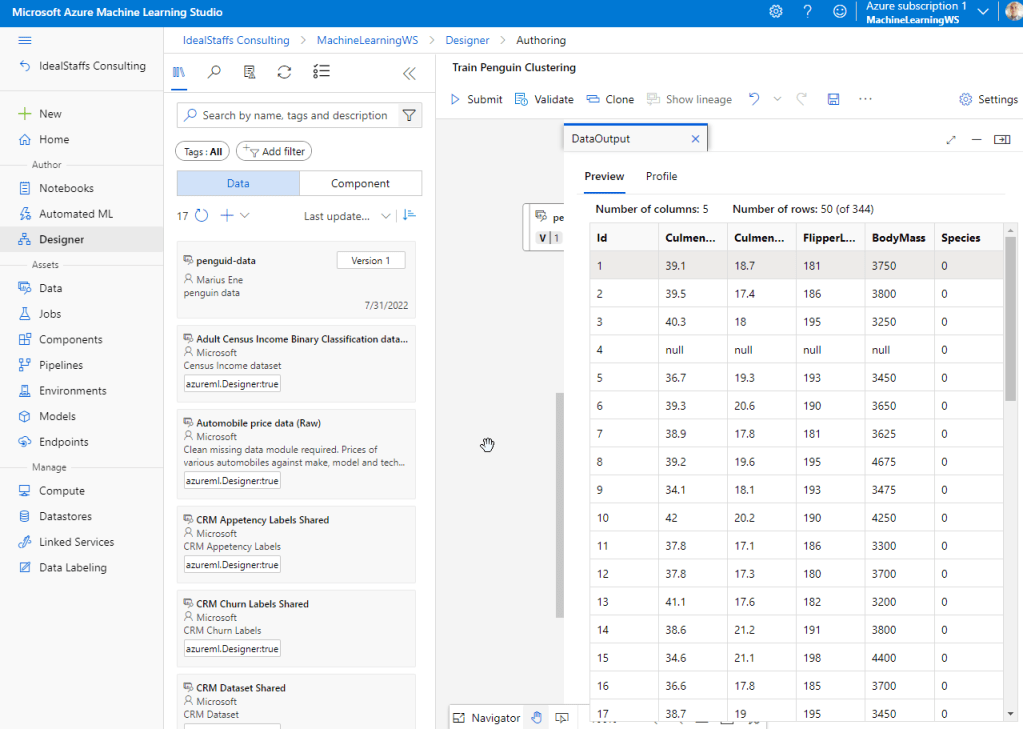
Drag the penguin data on the canvas.
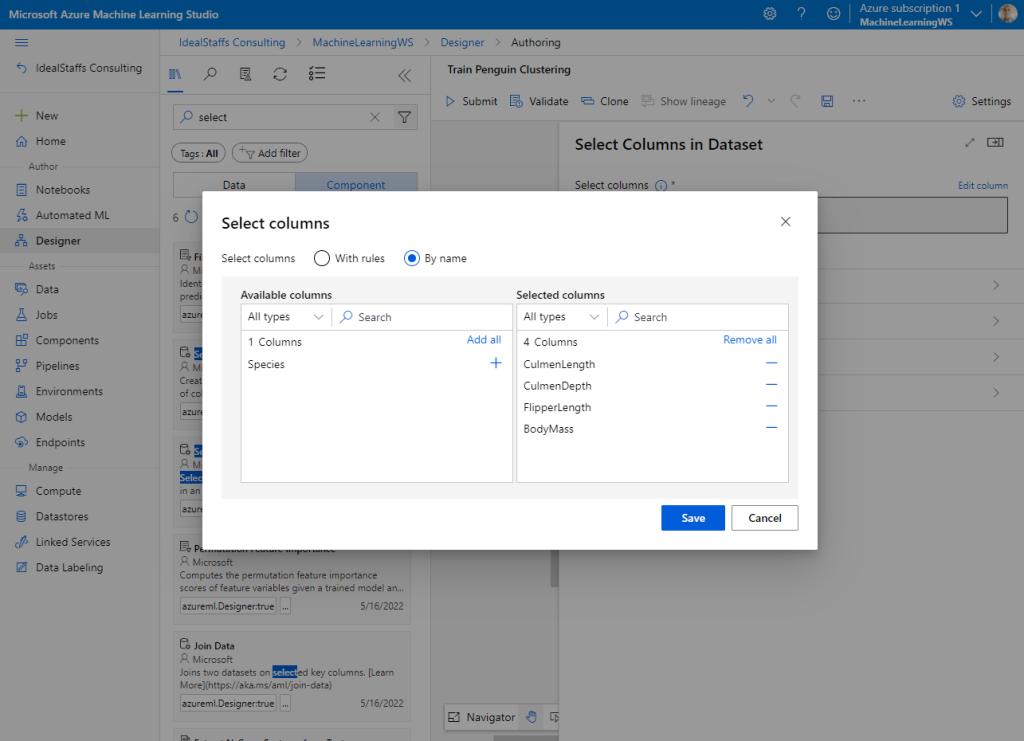
From the Asset Library we will add a component called Select Columns in Dataset.
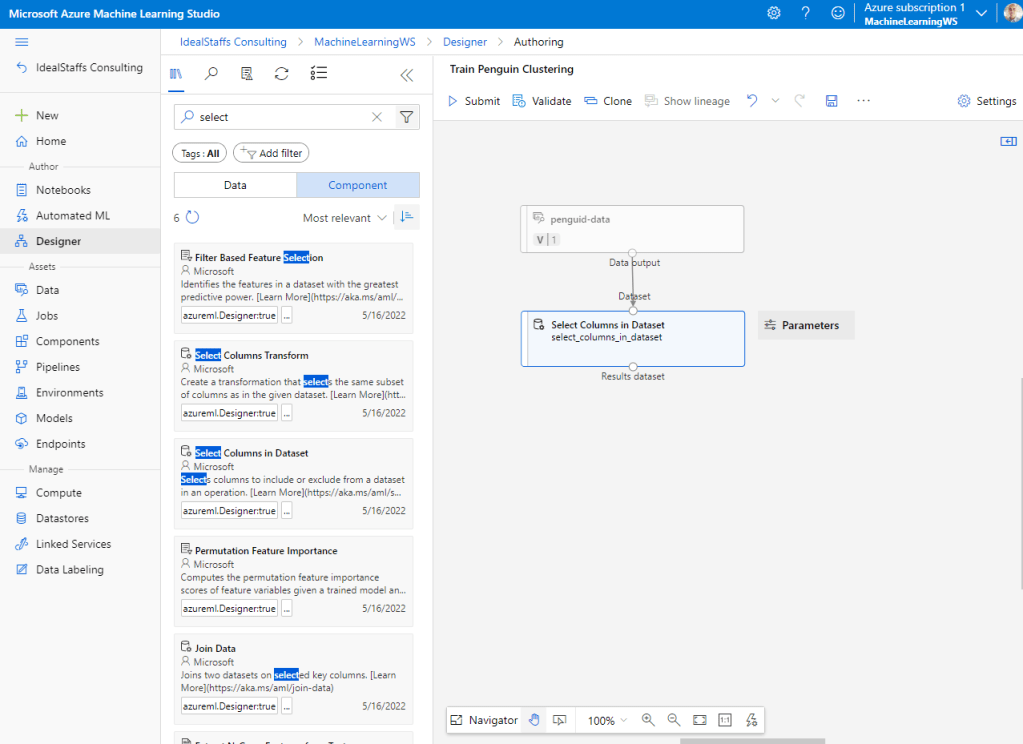
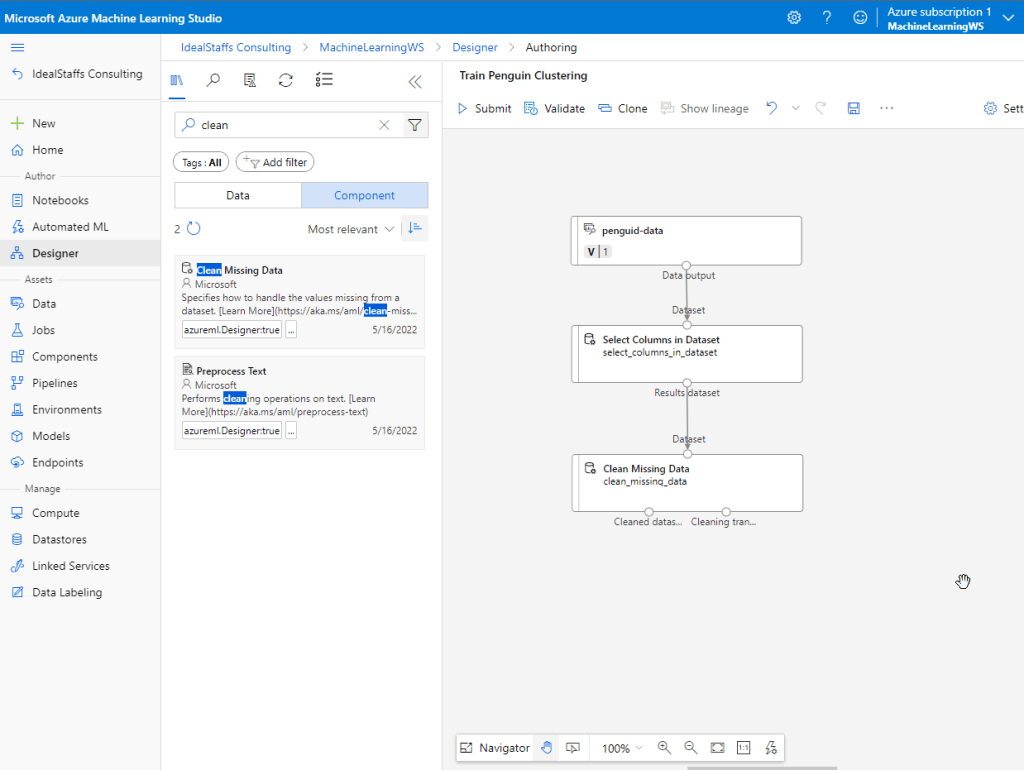
To cluster the penguin observations, we’re going to use only the measurements; so we’ll discard the species column. We also need to remove rows where values are missing, and normalize the numeric measurement values so they’re on a similar scale.
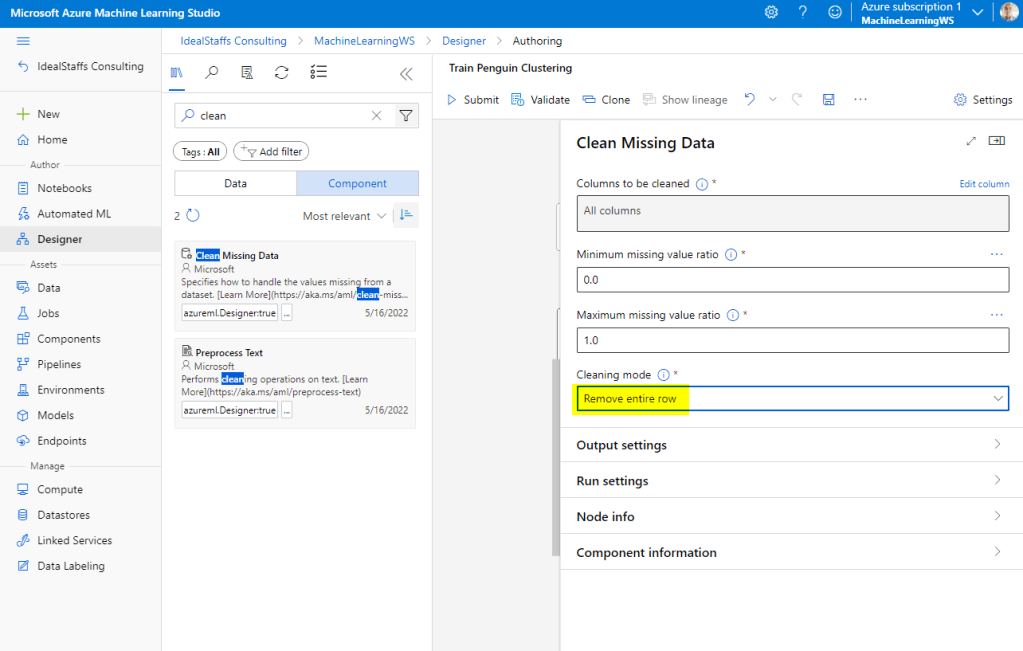
Add the Clean Missing Data module.
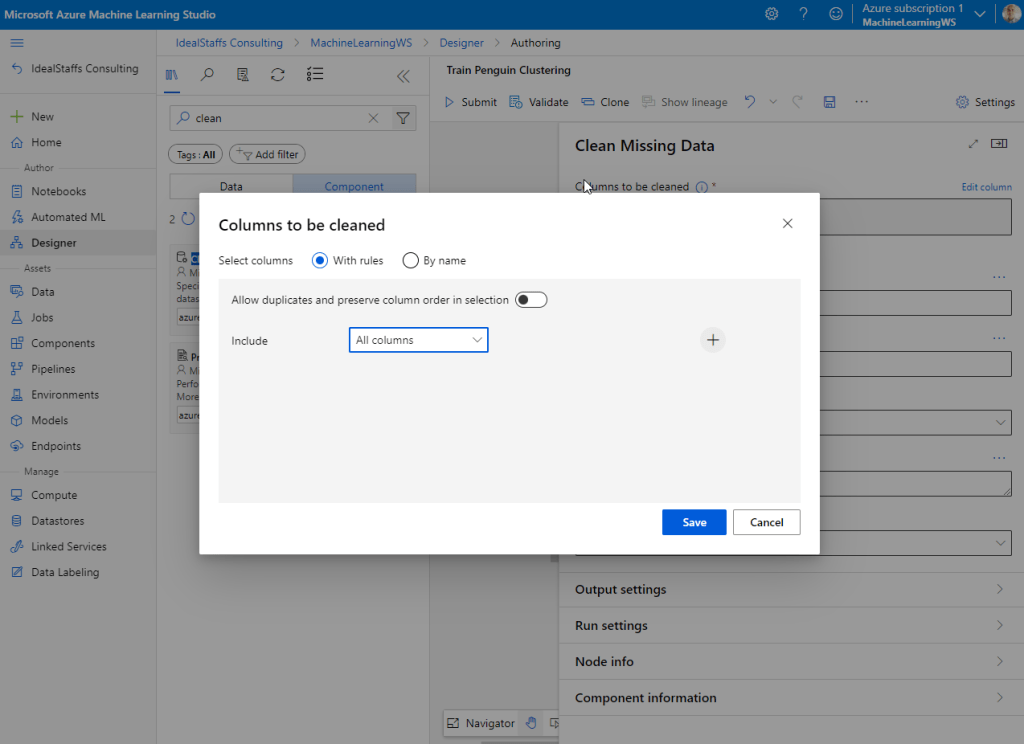
In the module properties, select All Columns
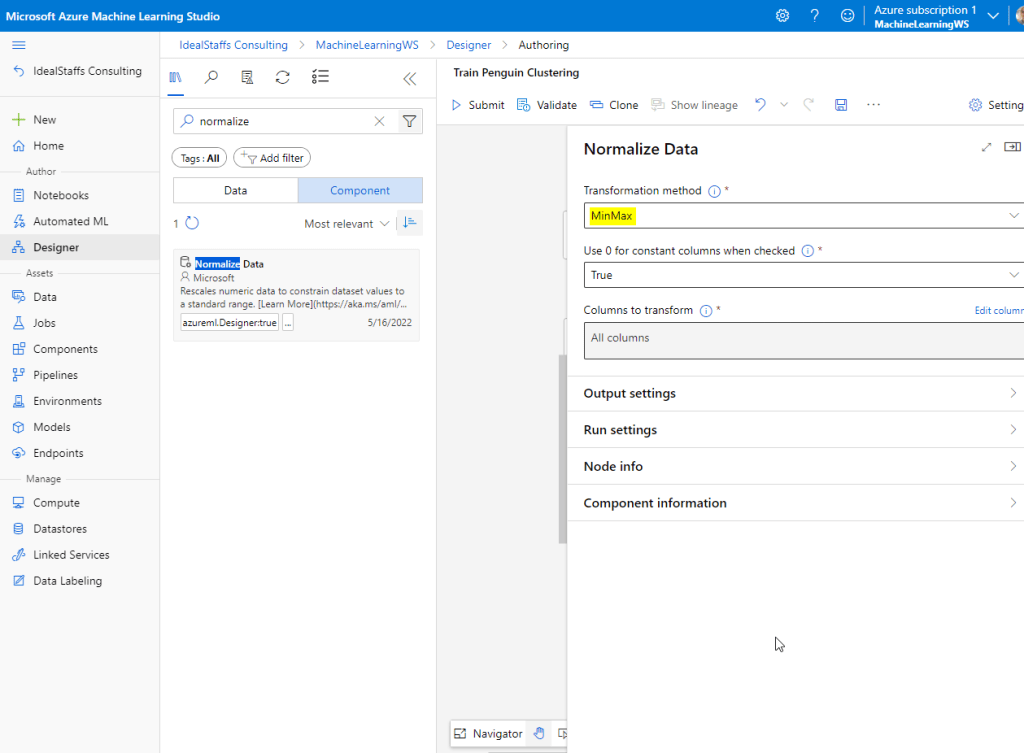
Add the Normalize Data module.

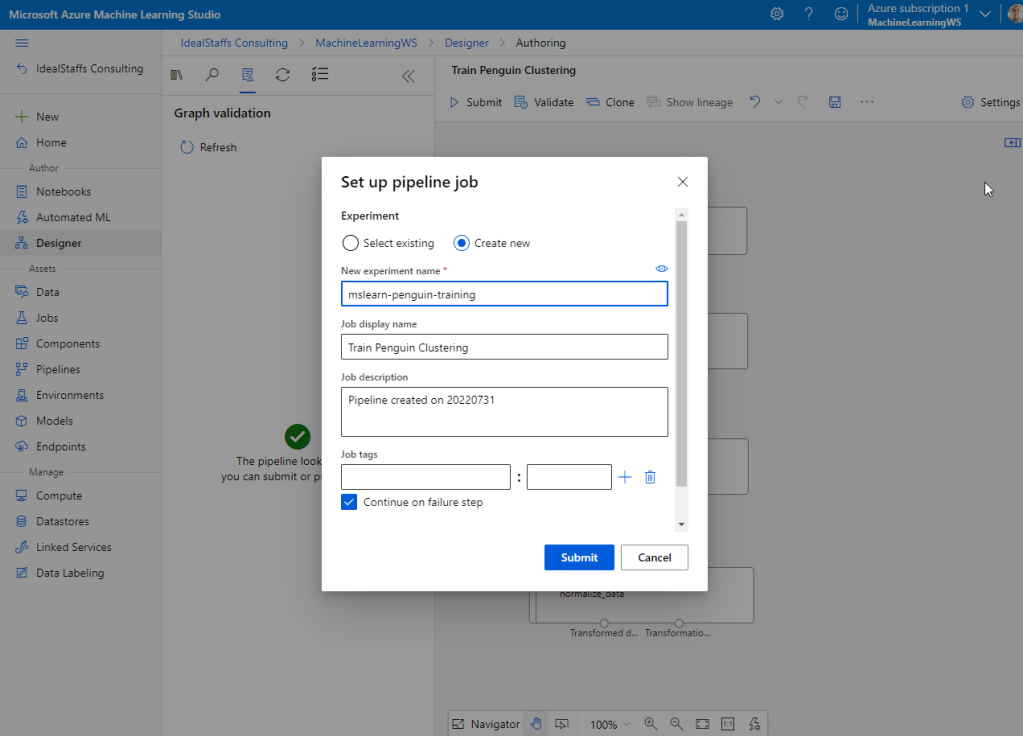
Submit to run the pipeline.
Adding training modules.
To train a clustering model, you need to apply a clustering algorithm to the data, using only the features that you have selected for clustering. You’ll train the model with a subset of the data, and use the rest to test the trained model.
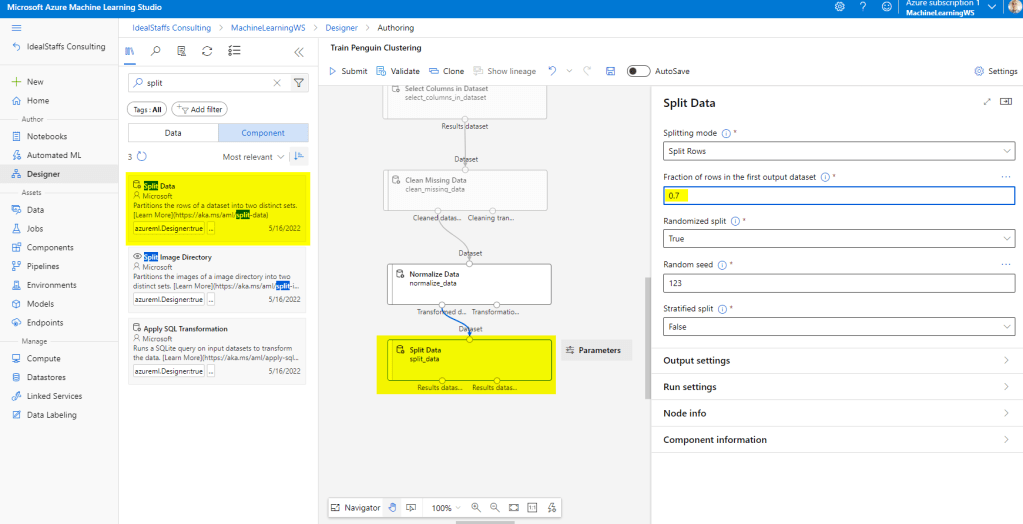
Add the Split Data module and configure it as below.
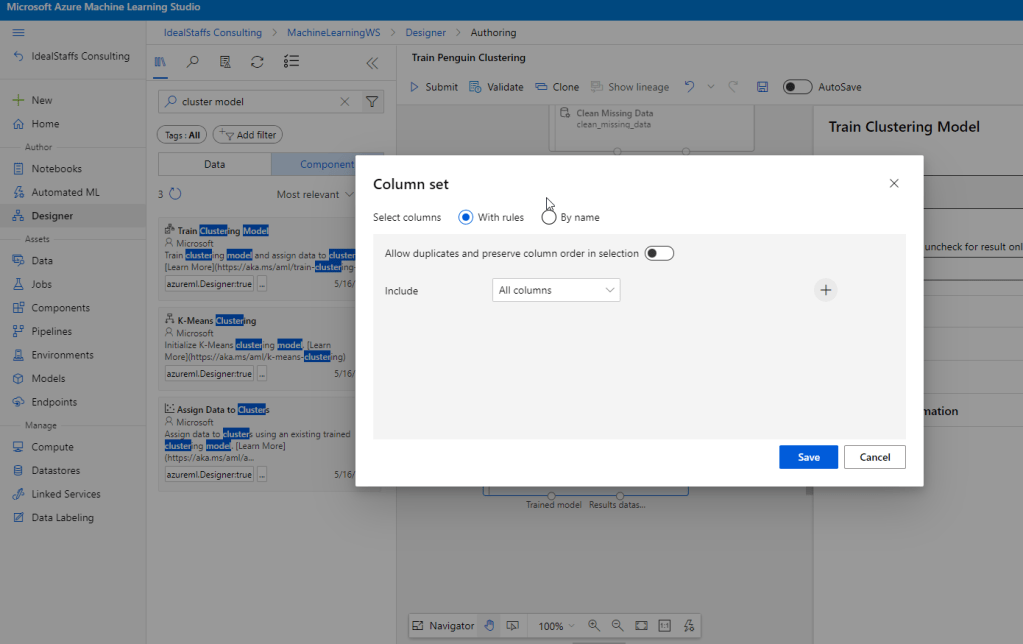
Add the Train Clustering Model module and configure it.
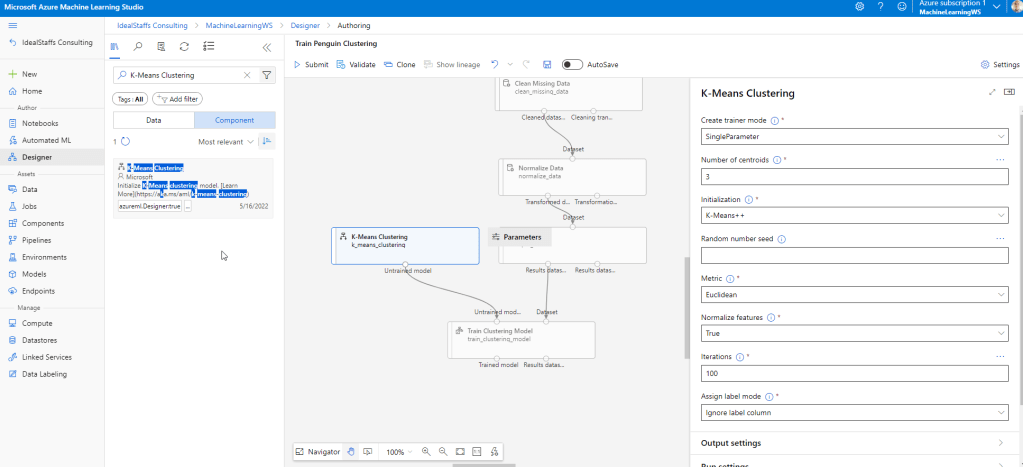
Add the K-Means Clustering module and configure it.
Add the Assign Data to Clusters module and configure it.

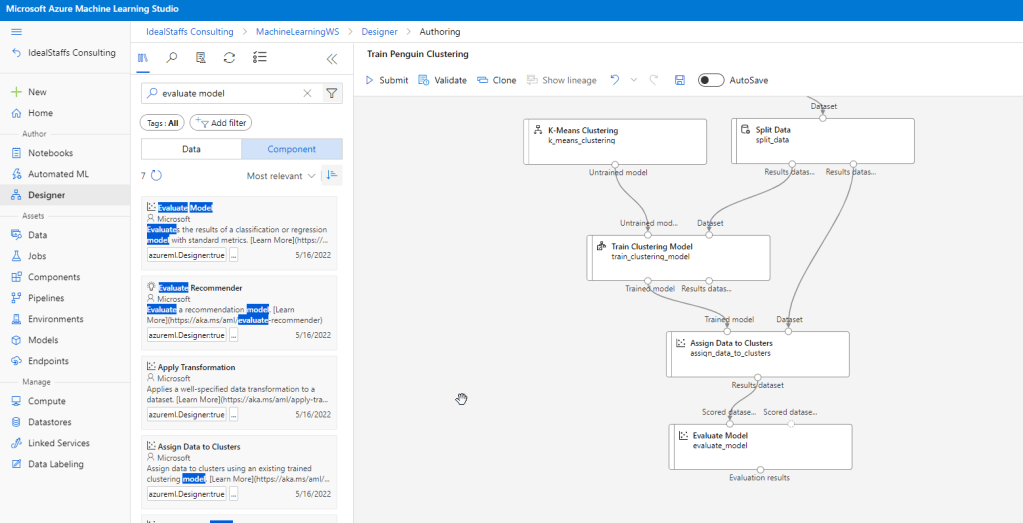
Submit, and run the pipeline using the existing experiment named mslearn-penguin-training on your compute cluster.
Evaluate the clustering model
Evaluating a clustering model is made difficult by the fact that there are no previously known true values for the cluster assignments. A successful clustering model is one that achieves a good level of separation between the items in each cluster, so we need metrics to help us measure that separation.
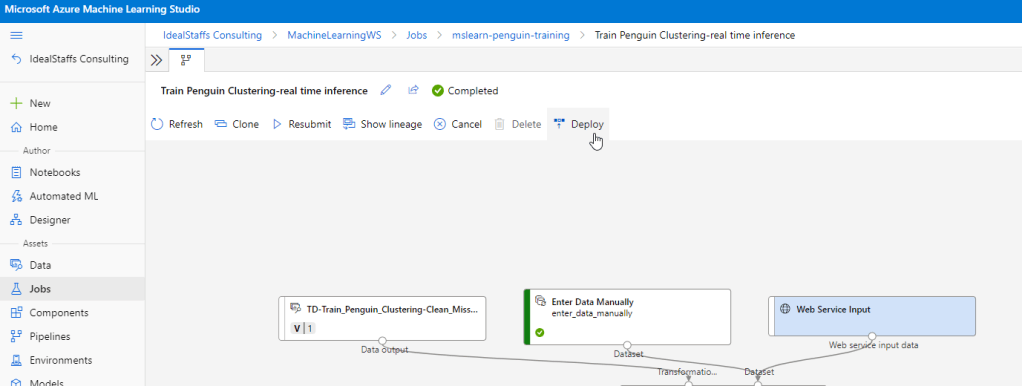
Create an inference pipeline
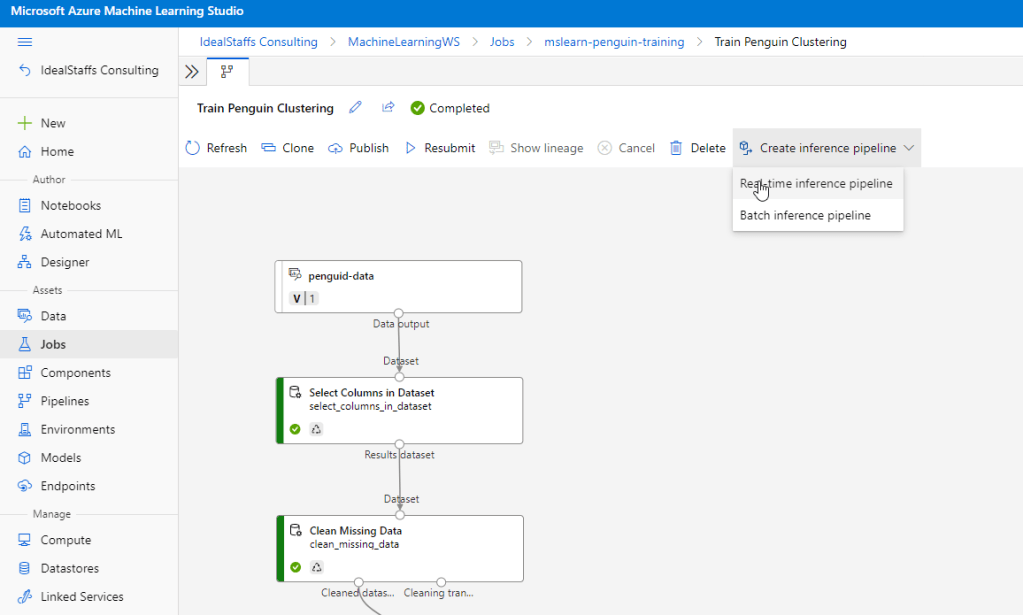
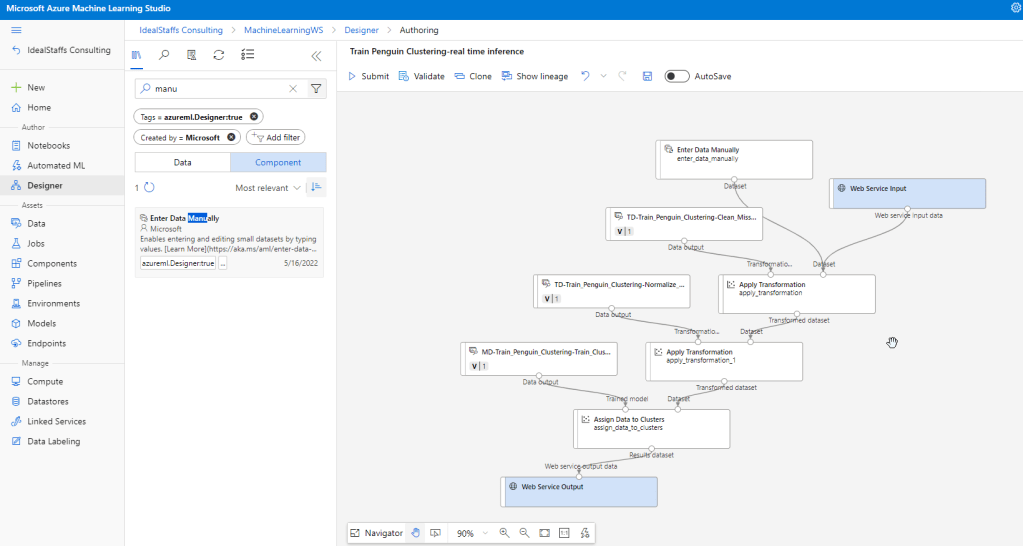
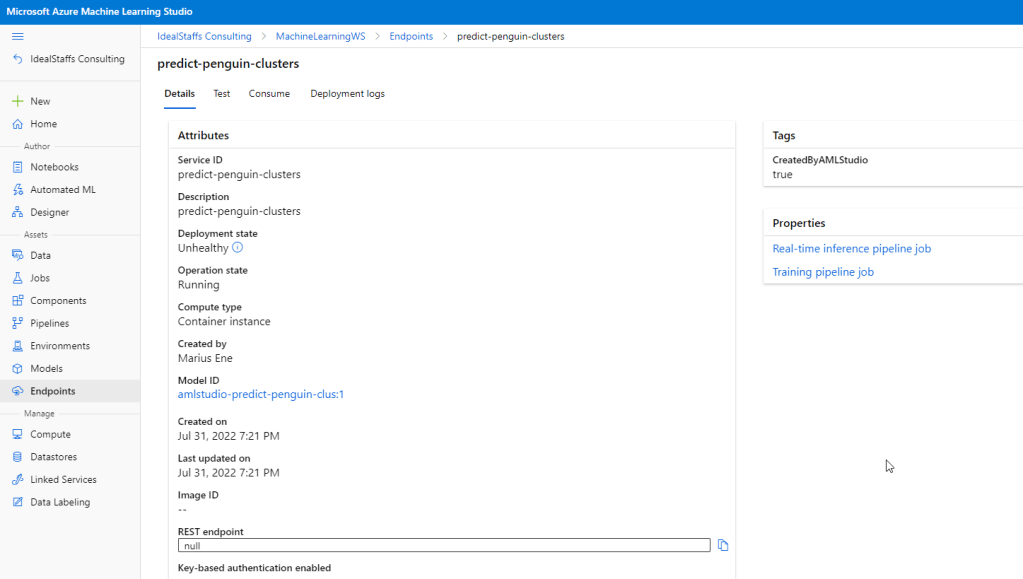
Deploy the service